Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for our well-being and general health. Unfortunately, our body lacks the ability to produce them by itself. As a result, we must rely on dietary sources to meet the daily recommended omega-3 intake. There are three main types of Omega 3: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
In this article, we will explore the difference between ALA and DHA, their unique health benefits and highlight the best dietary sources to obtain them. Additionally, we will offer guidance to those individuals who cannot incorporate these fatty acids into their diets and discuss dietary supplements as an alternative to ensure adequate intake.
What Are ALA and DHA?
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is the most common type of omega-3. It serves as the precursor of EPA and DHA, meaning that ALA is converted into these forms within the body. However, this conversion is not very efficient, with only approximately 3.8% of ALA being converted to DHA, making it challenging to meet the recommended daily intake of DHA solely from ALA. Any ALA that is not converted into EPA or DHA is utilized as an energy source in the body or stored as fat, similar to other fats.
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is particularly notable for its crucial role in brain health.
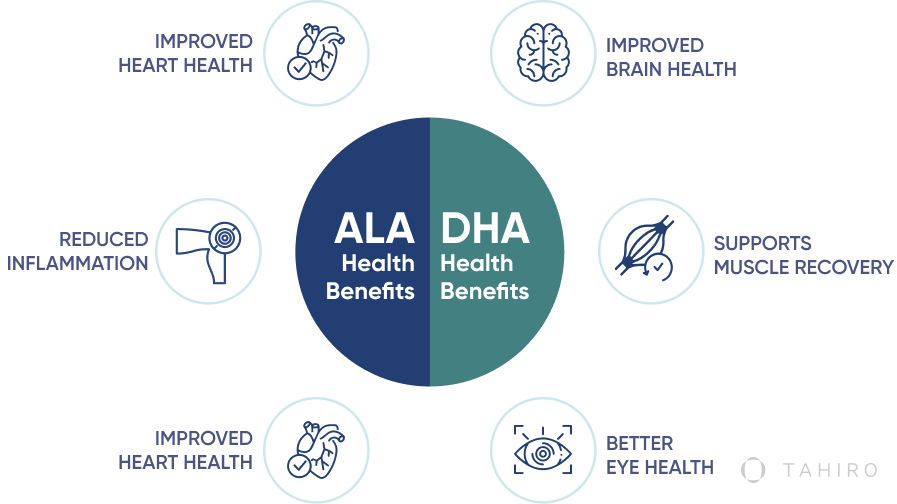
ALA and DHA Health Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids offer different health benefits. They have important roles in the body, such as reducing inflammation and improving heart health and brain function. Here are some of the health benefits seen for both ALA and DHA.
ALA Health Benefits
-
Improved heart health. It can decrease the risk of heart disease by reducing cholesterol levels, reducing inflammation, and increasing “good” cholesterol (2).
-
Reduced inflammation. Research shows that omega-3 may also help reduce inflammation, leading to decreased joint pain and enhanced immune function (3).
-
Improved heart health. Evidence shows (3) that ALA may help improve neurotransmitter function, improve mood, and reduce the risk of stroke.
DHA Health Benefits
-
Improved brain health. DHA plays a crucial role in brain development and function in childhood. It also helps improve brain health and decrease the risk of age-related conditions, such as Alzheimer’s (4).
-
Supports muscle recovery. Strenuous exercise can lead to an increase in inflammation, which can lead to soreness. In a study, women taking DHA had a reduction in muscle soreness by 23% (5).
-
Better eye health. DHA, along with other omega-3s, can help reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration (6). It may also help decrease dry eyes and retinopathy (diabetes eye disease).
Sources of ALA and DHA
A big difference between ALA and DHA is where you can find them. Generally speaking, ALA is found in plant-based sources, while DHA is mostly found in animal sources. Here are the main sources for each omega-3.
-
ALA: chia seeds, canola oil, flaxseeds, hemp seeds, soybean oil, walnuts, edamame, walnuts, sardines, salmon, beans, and shellfish.
-
DHA: salmon, mackerel, sardines, tuna, herring, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and sea bass.
What's The Difference Between ALA and DHA?
Besides its molecular structure, there are several differences between ALA and DHA. One of its differences is where you get them. ALA is mostly found in plant-based sources (with only a few animal sources), while DHA is mostly found in animal sources.
Another difference is that while the mechanism is highly inefficient, you can create DHA from ALA, but not vice versa.
Finally, as we’ve seen, while there are some similar health benefits, ALA may have a more positive effect on heart health, while DHA can have a greater impact on brain health. Keep in mind that there is currently more research stating the benefits of DHA than of ALA.
Do You Need Both ALA and DHA?
Yes, you need both since they are considered essential. While we’ve seen that ALA may get converted into DHA and EPA, the process is so inefficient it’s best to get them from food sources.
Remember that ALA and DHA are not the only omega-3 fatty acids that must come through your diet; EPA is also considered essential.
Which Omega-3 Fatty Acid Is Best?
So, if you need to focus on one, which one should you pick?
The answer is you should focus on all three of them. They all play a crucial role in the body, making each an essential player in overall health. That is why it’s important to add different dietary sources high in omega-3 to get different versions of omega-3.
If you are struggling to add different omega-3 source, the best way to guarantee you are getting enough omega-3 daily is to supplement.
The best dietary omega-3 supplement is Tahiro’s Omega-3. This supplement is made from algae, making it a great option for people who follow a traditional diet or a plant-based diet.
In addition, since it is made from algae, it contains all three essential omega-3s. So, you don’t have to worry about adding other sources to get your daily dose of ALA or DHA. You know that you get enough of both in a couple of capsules.
Finally, what makes this one of the top-notch supplements is that it comes from a sustainable source, and you won’t get unwanted reflux (which is commonly seen in fish oil supplements).