Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for health. They can help reduce inflammation and help support heart health. There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid
(EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
While all three are important, DHA and EPA have more impressive health benefits than ALA. But what are the differences between them? What are the possible health benefits of each one?
In this article, we will go over the differences between EPA and DHA, what their health benefits are, and determine if you need both in your diet.
What's The Difference Between EPA and DHA?
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are long-chain omega-3 fatty acids that are normally found in certain fish and algae. They are essential for human health since the body cannot produce them on its own.
Both EPA and DHA can be obtained through diet or supplementation, offering several health benefits, such as improved cognitive function and reduced inflammation.
While they are both vital for overall well-being, there are several key differences between EPA and DHA, including sources, functions, and health benefits. Here are some of the main differences.
-
Structure. The first difference is its structure. But to avoid getting too technical, the only thing you need to know is that EPA contains fewer double bonds than DHA.
-
Sources. EPA is more prevalent in certain types of cold-water fish, while DHA is mainly found in fatty fish (mackerel, salmon, and trout).
-
Health benefits. Thanks to its effects on reducing inflammation, EPA has been shown to help improve heart health and joint health. On the other hand, DHA has been shown to improve brain function and eye health.
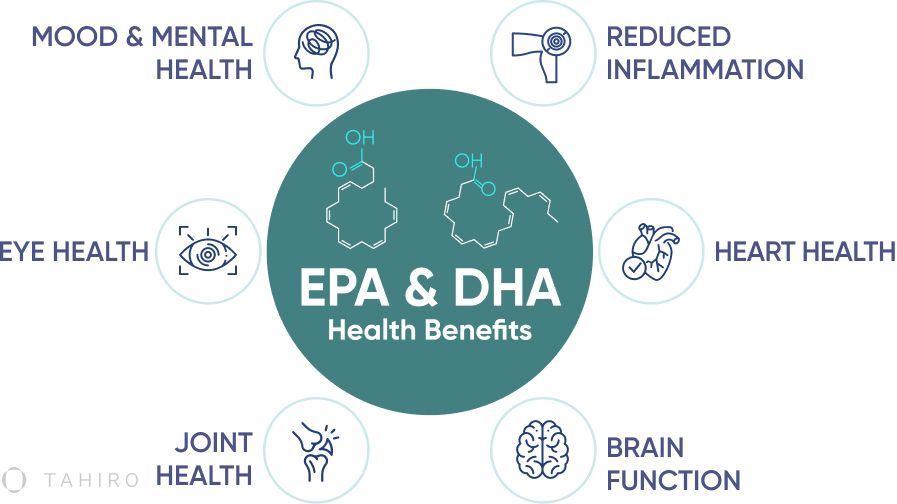
EPA and DHA Health Benefits
EPA and DHA provide a wide range of health benefits. Here are some of the health benefits you may obtain by adding EPA and DHA into your diet.
-
Reduced inflammation. Both EPA and DHA have anti-inflammatory properties, meaning they can help reduce inflammation (1). In addition, they can help enhance immune function.
-
Heart health. EPA is known for its cardiovascular benefits (2). It may help reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure, and reduce inflammation, resulting in improved heart health. While EPA is the main contributor to heart health, DHA can also help lower triglycerides, helping lower the risk of heart disease.
-
Brain function. DHA is a crucial component of brain cell membranes and plays a vital role in brain development (3), especially during pregnancy and early childhood. It seems that DHA may help support cognitive function, learning, and memory.
-
Mood and mental health. EPA has positive effects on mood and mental health. In fact, in some cases, it is recommended as a dietary supplement for people with depression or anxiety (4).
-
Eye health. DHA is a vital component of the retina, which helps maintain normal vision. DHA may help protect against age-related macular degeneration and other vision-related conditions (5).
-
Joint health. Thanks to its anti-inflammatory properties, EPA can help reduce joint pain and stiffness in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis (7).
It’s important to understand that while both EPA and DHA have several health benefits, the specific advantages of each may vary. To achieve these benefits, include sources of omega-3 fatty acids or add an omega-3 supplement.
However, when adding a supplement, consult a health professional to determine the best dosage and ratio for your needs.
Do You Need Both EPA And DHA?
Yes, you need both EPA and DHA for optimal health. While both options are essential and provide several health benefits on their own, they often work best together to support overall well-being.
Are DHA and EPA From Natural Sources Better Than Supplements?
The choice between obtaining EPA and DHA from natural sources or supplements depends on several factors. Here are some things you need to consider.
Natural Sources
Pros
-
Whole nutrition. When you get DHA and EPA from natural sources, you get other nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats.
-
Low risk of contaminants. Whole foods, mainly those from wild-caught sources, tend to be lower in contaminants and heavy metals than some fish supplements. However, keep in mind that this is not the case with algae-based supplements.
Cons
-
Calories. Natural sources of omega-3 tend to be high in fat, resulting in foods with a high caloric content. If you are not careful and eat them in moderation, it may result in weight gain.
-
Variability. The omega-3 content can depend on the dietary sources. So, it can be challenging to get a consistent dose every day.
-
Contaminants. Farmed-raised fish can be high in contaminants and heavy metals.
Supplements
Pros
-
Precision and consistency. Omega-3 supplements offer a precise and consistent dose of DHA and EPA.
-
Convenience. Supplements can be a convenient way to ensure you get an adequate amount of DHA and EPA, especially when having dietary restrictions (vegans or allergic to seafood).
-
Purity. High-quality supplements are purified and tested for contaminants, ensuring that you are not exposed to harmful levels of toxins.
Cons
-
Lack of nutrient synergy. Supplements provide EPA and DHA in isolation. This means you won’t get other nutrients from the supplement.
-
Cost. High-quality omega-3 supplements can be quite expensive, especially if taken regularly over an extended period.
-
Digestive issues. Some people may experience digestive issues, especially when taking fish-based supplements. This is not widely seen in algae-based supplements.






