While many people believe that inflammation harms our bodies, it is important to recognize that inflammation is a natural response by our body’s immune system to protect us from infection and injuries. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to several health problems, including heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and obesity (1). Therefore, managing and reducing chronic inflammation is essential for maintaining good health and overall well-being.
Nutrition and healthy lifestyle habits are important key factors for helping reduce inflammation. Research and studies heavily support the Potential of omega-3 fatty acids in reducing inflammation. Unfortunately, our bodies cannot produce them, and the best way to obtain these essential fatty acids is through natural foods and supplements.
In this article, we will explore the potential health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids in reducing inflammation, and the recommended intake amount, and answer an important question: Should you consider taking omega-3 supplements?
Does Omega-3 Reduce Inflammation?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for our health. There are three main types of omega-3: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
According to research (2), omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory benefits, helping reduce inflammation. They earned the respectable title “essentials” since our body cannot produce them by itself, meaning we must get them through diet. Other known health benefits of omega-3 can be found in this article.
How Does Omega-3 Reduce Inflammation?
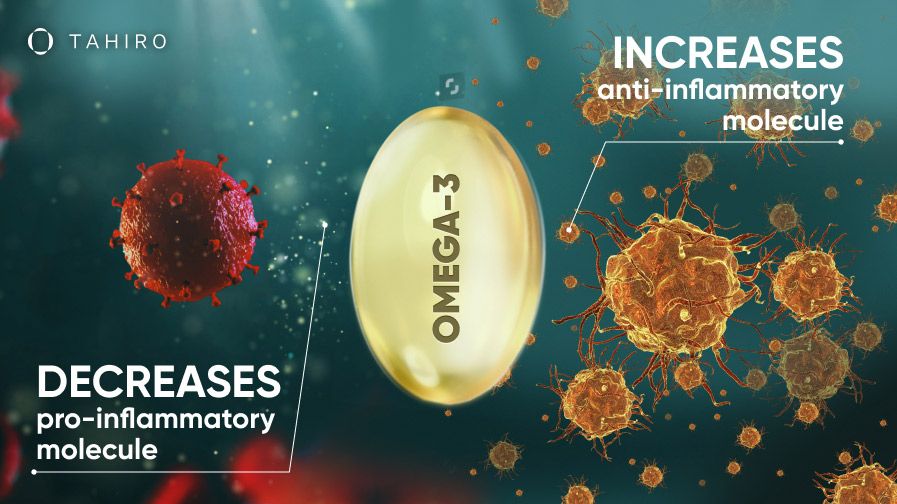
Omega-3 fatty acids are linked to reducing inflammation because they can influence the production of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory molecules.
Evidence suggests that omega-3 fatty acids can lower the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines and prostaglandins (3). In addition, omega-3 promotes the production of anti-inflammatory molecules, such as resolvins and protectins (4).
These omega-3 properties can help balance the body’s inflammatory response, reducing the risk of chronic inflammation-related disease.
Can Omega-3 Cause Inflammation?
Omega-3 fatty acids cannot cause inflammation by themselves. While omega-6 fatty acids are also considered essential, an imbalance between omega-6 and omega-3 can lead to inflammation and contribute to several health issues.
Due to the consumption of highly processed foods, the modern Western diet often contains an overabundance of omega-6-rich foods. On the contrary, the average diet does not contain enough omega-3 fatty acids. This imbalance often causes inflammation in humans.
To achieve a healthy balance between the two, it is recommended that you avoid consuming foods with high omega-6 and include more omega-3 sources.
How Much Omega-3 Should You Take to Reduce Inflammation?
The recommended daily intake of omega-3 fatty acids can vary depending on several factors, such as age, gender, dietary preferences, and specific health conditions. However, a recommended intake of 250-500 milligrams of DHA and EPA can bring several health benefits (5).
But, as previously mentioned, remember that the intake of omega-3 is not the only key factor. The ratio between omega-6 and omega-3 is also crucial for overall wellness.
Speak with a healthcare provider to determine your needs and create a dietary plan that aligns with your health goals.

Can Omega-3 Supplements Help Reduce Inflammation?
Omega-3 supplements are a great way to help reduce inflammation. These supplements offer a convenient way to increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids and benefit from their anti-inflammatory properties.
The supplements may help promote a healthy balance between omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, bring a healthy balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory molecules, and help protect against neuroinflammation (brain inflammation).